In this article
What is a Piping and Instrumentation Diagram?
A piping and instrumentation diagram, also called P&ID, is a diagram used to show a graphical display of a complete system. It includes all piping, instruments, valves, and equipment the system consists of. Through a P&ID, you can get the following information:
- The mechanical and electrical details of a given system or process,
- Piping information such as sizes and material specifications,
- Continuation flags leading to the connecting P&IDs,
- Flow arrows, DCS alarm types
- The connection types from the controllers to the field devices,
How to Read P&IDs?
Here are a few aspects you should consider while reading a piping and instrumentation diagram. You need to know what P&ID symbols mean and how each symbol is constructed using graphical elements and connecting lines. If you can do this, reading a piping and instrumentation diagram won't be difficult.
#1 Know the Letter and Number Combinations of a P&ID
Letter and number combinations appear inside each graphical element, and the ISA standard defines letter combinations. Numbers are user-assigned. The first letter represents the measured or initiating variables, such as Analysis (A), Flow (F), Temperature (T), etc., with succeeding letters defining readout, passive, or output functions, such as Indicator (I), Record (R), Transmit (T), and so forth.
Tag numbers are a combination of alphabets and numbers with varying lengths that aid in identifying the device, what it controls, the type of device, and the number with which it is registered on the P&ID. Physical instruments are indicated by a tag number and a circle around them. These numbers are also used to locate the position of equipment.
The order and letters in tag numbers are highly specified and unique for each device. The first digit/letter specifies the factors controlled and monitored by the device, while the second digit indicates the type of device. The letters 3,4 and 5 elaborate on the device’s function and hint about the following few numbers in the series.
Standard Abbreviations Used in P&ID
Abbreviations are introduced in a P&ID to keep the diagrams concise and straightforward. The table below constitutes some commonly used abbreviations.
| AC | Analysis Controller | PB | Push-button |
| AE | Analyzer Element | P/I | Pneumatic To Current Converter |
| AAH | Analysis Alarm [High] | POV | Pneumatically Operated Valve |
| BE | Burner Element | pHT | pH Transmitter |
| BDV | Blowdown Valve | PSE | Rupture Disk |
| CR | Conductivity Recorder | PR | Pressure Recorder |
| ES | Electrical Switch | PZV | Pressure Relief Valve |
| FIT | Flow Indicator Transmitter | RC | Ratio Controller |
| FY | Computer, Relay, Amplifier or I/P Converter, etc. in Flow Loop | RO | Restriction Orifice |
| I/I | Current Indicator | RTD | Resistance Temperature Detector |
| KI | Clock/Timer | SA | Speed Alarm |
| LCV | LCV Level Control Valve | SD | Shutdown Panel |
| LIT | Level Indicator Transmitter | SV | Solenoid Valve |
| LO | Lock Open | TA | Temperature Alarm |
| MCC | Motor Control Center | TCV | Temperature Control Valve |
| MT | Motion Transmitter | TH | Thermostat |
| MTU | Master Terminal Unit | US | Utility Station |
| NC | Normally Closed | WE | Weight Measuring Element |
| NO | Normally Open | WS | Water Supply |
| PA | Pressure Alarm | ZV | Safety Shut-down (Pilot) valve |
#2 Identify and Understand Standard Equipment -Instruments
Knowing how to read the symbols and shapes in the drawing is also essential. EdrawMax provides all kinds of symbols required in P&IDs.
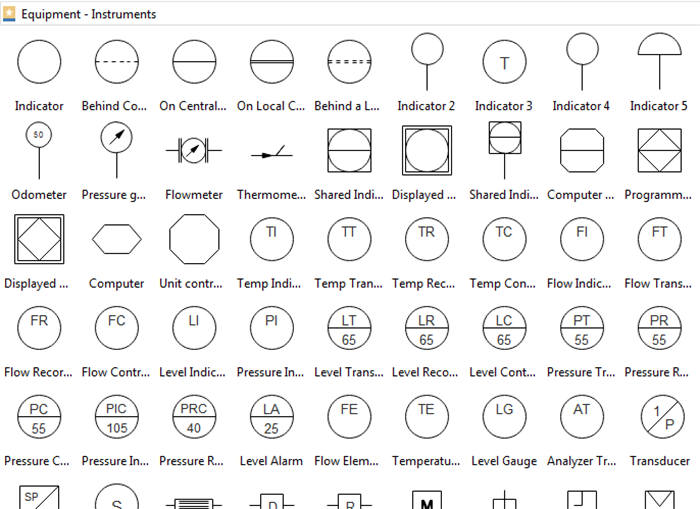
All the instruments in a P&ID are marked by a circle with an assigned tag number and line inside. The tag number helps in identifying the device, whereas the line is the location indicator. Lines are classified into different types, each describing the device's location with respect to the field. The types of lines used in a P&ID are given below.
Instruments Location
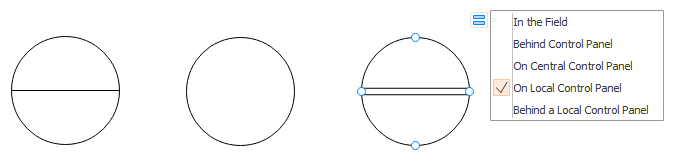
- No line: A simple circle indicates that the device is in the field and is a locally mounted instrument. The device is observable in the field and is accessed by the operator.
- Solid Line: A solid line in the center signifies that the instrument is placed in a primary location in the control room. The instrument is visible on the front of the panel or video display.
- Dashed Line: The dashed line specifies that the instrument is in a secondary position in the control room and inaccessible to the operator. It is not visible on the front of the panel or video display.
- Double Solid Line: A double solid line tells that it is in a primary position in the local control center and is operator accessible at the panel front or console.
- Double Dashed Line: A double dashed line describes that the instrument is in a secondary position in the local control center and is not operator accessible. The device is located in the field cabinet and is not visible on the front of the panel or the video display.
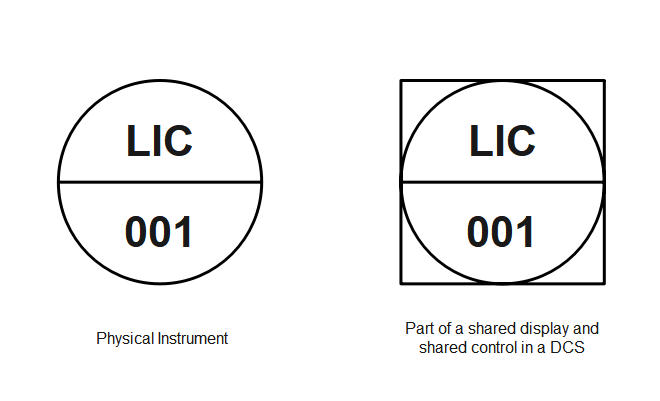
Shared Display and Shared Control
Shared display means when the same information can be viewed and accessed from different locations in a network. Shared control indicates that the user can interact with the system and modify the operational conditions remotely. To represent an instrument with a shared control and display system, take the tag number and draw a square around it. This indicates that the instrument can now be accessed remotely in a Distributed Control System (DCS).
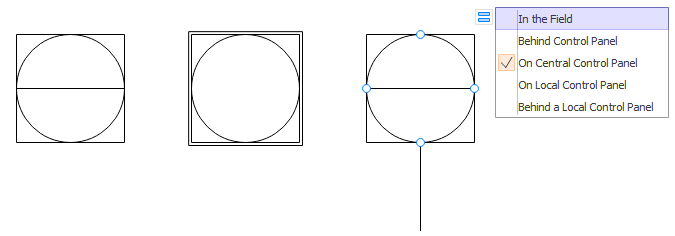
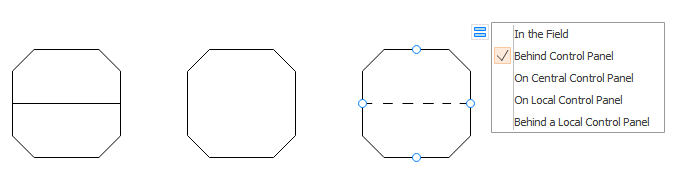
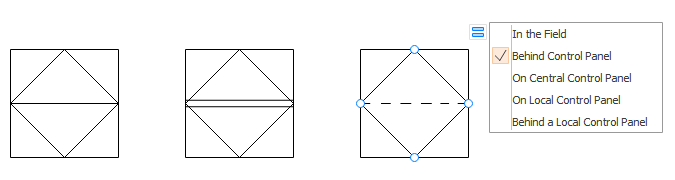
According to ISA S5.1, there are mainly 4 four graphical elements: discrete instruments, shared control/display, computer function, and programmable logic controller. Circular elements indicate discrete instruments. Shared control/display elements are circles surrounded by a square. Computer functions are indicated by a hexagon, and programmable logic controller (PLC) functions are shown as a triangle inside a square. These shapes represent both the physical and the software devices. In either case, it implies all the shapes needed in a piping and instrumentation diagram. You will see these shapes anytime a system is shown on the P&ID.
- Discrete instruments
- Shared control/display
- Computer function
- Programmable logic controller
#3 Learn to Use Graphical Elements and Connecting Lines
The connections between elements help engineers identify a particular pipe in a standardized way. Different colors indicate different pipes to avoid confusion. Adding a single horizontal bar across any of the four graphical elements suggests that the function resides in the primary location category. A double line indicates an auxiliary location; devices behind a panel board in some other inaccessible location are shown with a dashed horizontal line.
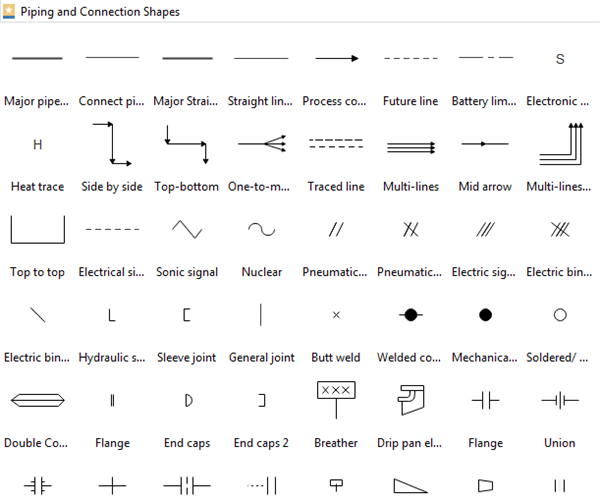
The connection lines on a P&ID elaborate on the associations between instruments: how they connect to each other and the type of signal being transmitted. For example, a solid line signifies the connection is via pipes, while a dashed line indicates electrical transmission. Knowing the symbols is essential to understanding the P&ID charts correctly. Here are the primary line types used to connect different devices/instruments.
| Major Process Piping |  |
| Minor Process Piping |  |
| Electrical Signal | 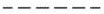 |
| Mechanical Link |  |
| Electromagnetic (Guided) Wave |  |
| Electromagnetic (Unguided) Wave | 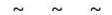 |
| Pneumatic Signal |  |
| Software or Data Link |  |
| Capillary Tubing |  |
| Hydraulic Tubing |  |
If you want to know more about Piping and Instrumentation Diagram or EdrawMax, welcome to experience.

EdrawMax is a powerful, all-in-one, easy-to-use diagramming tool that enables users to visualize ideas effortlessly.
EdrawMax provides beginners and pros with cutting-edge functionalities to build professional-looking diagrams easier, faster, and cheaper! It allows you to create more than 280 types of diagrams and should be an excellent Visio alternative.
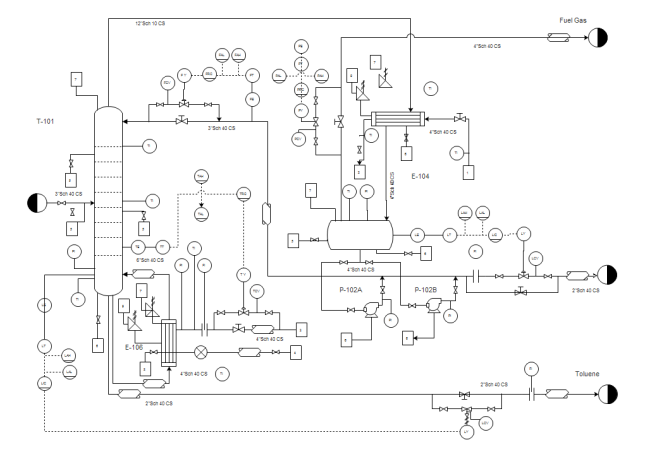
Piping and Instrumentation Diagram Examples
Here are some famous P&ID examples created by EdrawMax, which you can download and customize for free. To get more P&ID examples and templates, visit our Template Community.
- Plant P&ID
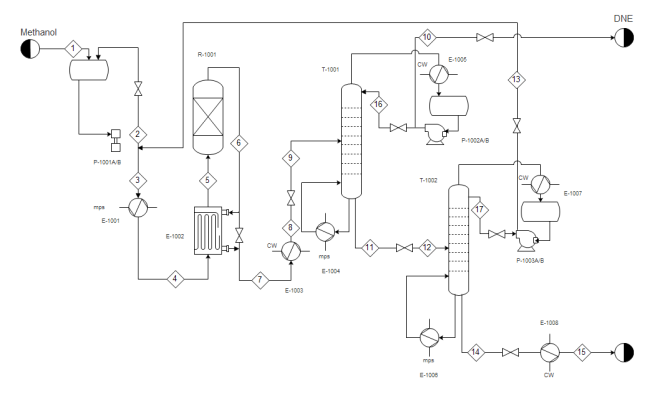
- Water Boiling Process P&ID
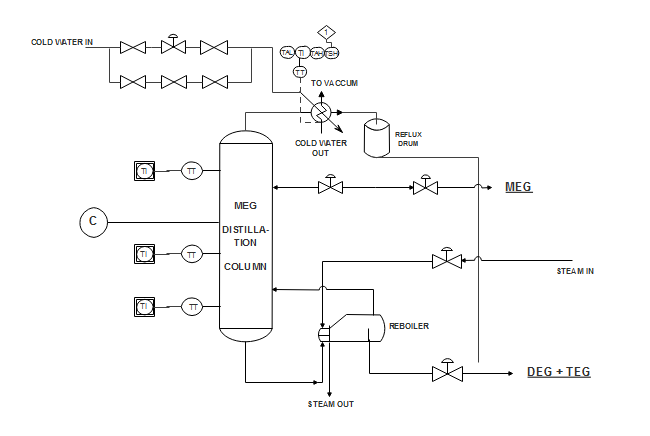
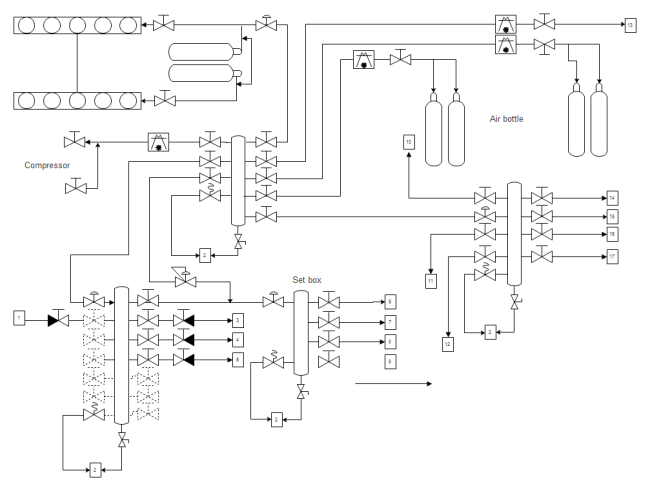
- System P&ID
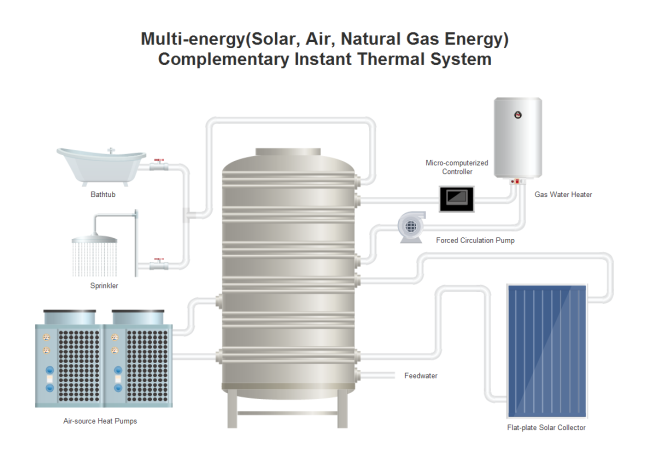
- Thermal System P&ID
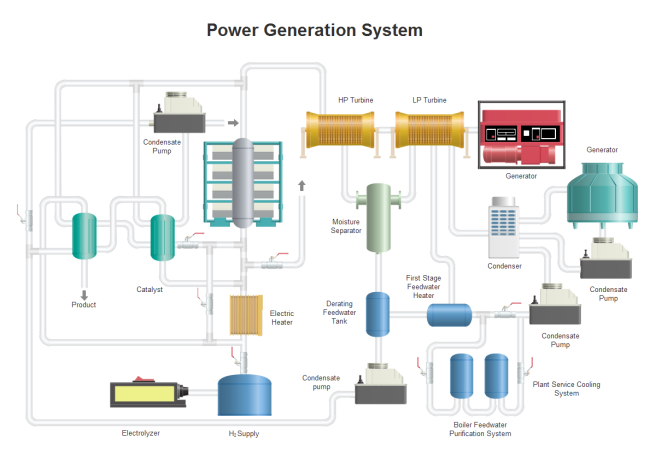
- Power Generation P&ID
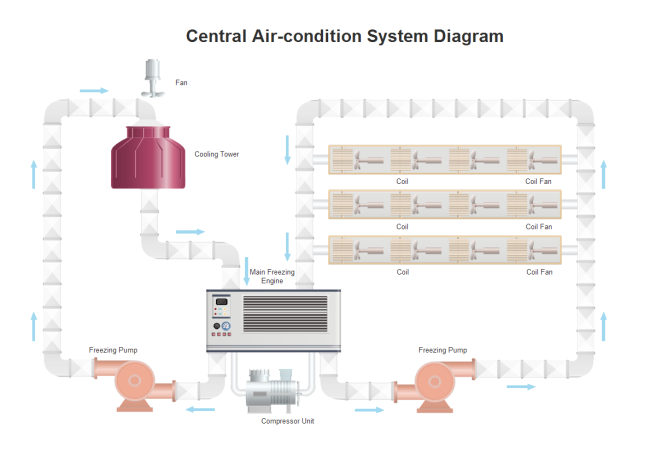
- Air Condition Process P&ID
EdrawMax is the versatile diagram software that integrates 100% functionality and libraries of all other drawing products.





