7 Best Organizational Structure Examples

Picking the best organizational structure for your company, division, or team is as important as constructing a company from the first brick.
It some point, you're continually searching for something road commendable - something that can take you (and your employees) from direct A toward point B effortlessly. A company works best with a various leveled organizational structure. Numerous sorts of organizational outlines exist because multiple kinds of organizational structures exist.
How about we see what is an organizational structure and the seven most used organizational structures and the reasons why you should use one?
EdrawMax provides you with many examples/templates for organizational structure.
What is an organisational structure?
The ordinarily progressive game plan of lines of power, correspondences, rights, and obligations of an association. Organizational structure decides how the jobs, force, and duties are delegated, controlled, and facilitated, and how data flows between the various degrees of management.
A structure relies upon the association's targets and procedure. In a brought-together arrangement, the top management layer has the vast majority of the decision-making power and has tight authority over departments and divisions. In a decentralized structure, the decision making power is dispersed, and the departments and divisions may have various degrees of autonomy.
An organizational diagram outlines the organizational structure.
Types of Organizational Structures
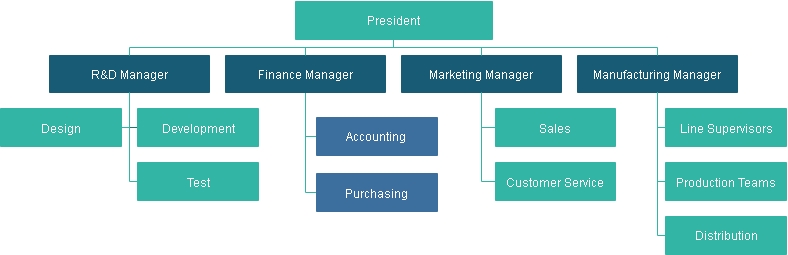
1. The functional organizational structure
A functional organizational structure begins with positions with the most significant responsibility levels at the top and goes down from that point. However, employees are sorted out as per their particular abilities and their relating capacity in the company. Each different department is overseen freely.
Pros
- Permits employees to concentrate on their job.
- Empowers specialization.
- Help teams and departments feel self-decided.
- It is effectively versatile in any measured company.
Cons
- It can make storehouses inside an association.
- Hamper's inter-departmental correspondence.
- Clouds procedures and strategies for various markets or items in a company.
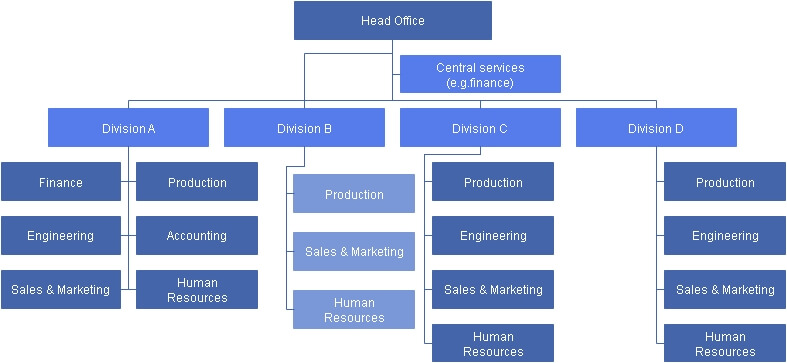
2. The multidivisional organizational structure
A multidivisional organizational structure adjusts a company as indicated by singular divisions, which depend on geographic areas, items, or administrations. As another option, an assembling company may actualize an item based divisional structure that includes the link get together and item designing divisions. Interestingly, an expert administration company may sort out around administration lines, for example, the individual and business administration divisions.
Pros
- Capacity to consider ranking directors responsible for the aftereffects of neighborhood tasks that are inside their control.
- Every division is aware of progress in the market, enabling the division to react to these shifts rapidly and stay serious by pulling together their working endeavors to changing shopper inclinations.
- To improve the division's responsiveness, decision-production lies at the division level. With attention to the nearby market, every division can create and deliver products and enterprises that intrigue its market and that the division produces and ships utilizing neighborhood assets.
Cons
- The duplication of capacities, such as deals or assembling, at every division, blocks the accomplishment of corporate-level economies of scale and increments working expenses.
- The repetition of capabilities can likewise prompt an absence of normalization and wasteful aspects.
- Almost certainly, division-explicit corporate motivating forces, for example, rewards, will prompt division contentions, which may bring about one division undermining the tasks of another division.
3. The matrix structure
A matrix organizational outline resembles a network, and it shows cross-practical teams that structure for different activities. For instance, a specialist may generally have a place with the designing department (drove by a building chief) yet chip away at an impermanent venture (pushed by an undertaking supervisor). The grid organization outline represents both of these jobs and announcing connections.
Pros
- Permits bosses to effortlessly pick people by the requirements of an undertaking.
- Gives an increasingly powerful perspective on the association.
- Urges employees to utilize their abilities in different limits besides their unique jobs.
Cons
- Presents a contention between department supervisors and venture chiefs.
- Can change more much of the time than other organizational graph types.
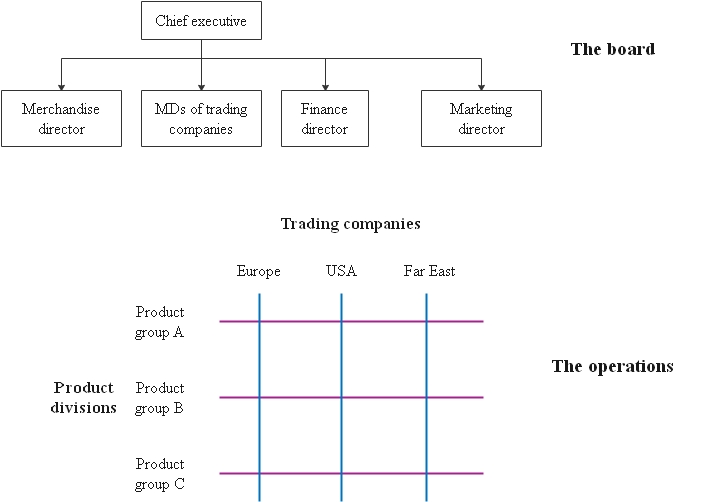
4. The holding company structure
A holding company exists exclusively to hold a percent of an absolute load of another company. Every auxiliary business inside the holding company has a useful structure holding organizations that are adaptable and can sell portions of powerless organizations without any problem. Those problems are hard to oversee since numerous individual organizations work inside their degrees.
Pros
- The structure of a holding company is proper for huge associations with holdings in a few different organizations working in various ventures.
- Holding company structures are regular in rough outside conditions where the rich treasury oversees spending plans and assets for its auxiliaries.
Cons
- Top management isn't in every case, clear on how much power and control to provide for division chiefs.
- There is an absence of strategy consistency among divisions and the potential for expanded expenses because of duplication capacities.
- As per the book, another considerable inconvenience of the divisional structure is that the global company frequently thinks it's hard to keep up a general corporate picture.
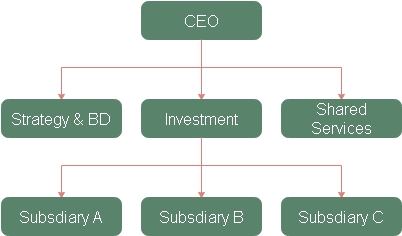
5. The transnational structure
In a transnational structure, you accomplish combination by selecting explicit sorts of troughs. Your nation or local administrators go about as a point of convergence for clients and regulate all items and capacities acted in their general vicinity.
Pros
- Organizations make changes to improve the nature of items or administrations offered at the neighborhood level.
- Providers, merchants, and different sellers search out associations with these organizations since it gives them an approach to venture into new markets.
- It is additionally an approach to ensure quality.
Cons
- Incredibly hard to adjust the necessities of various practical, topographical, and item partners.
- The order structure utilized by transnational associations can make vagueness and strife.
- Moreover, the intricate structure also genuinely frustrates decision-production forms due to the association of different individuals.
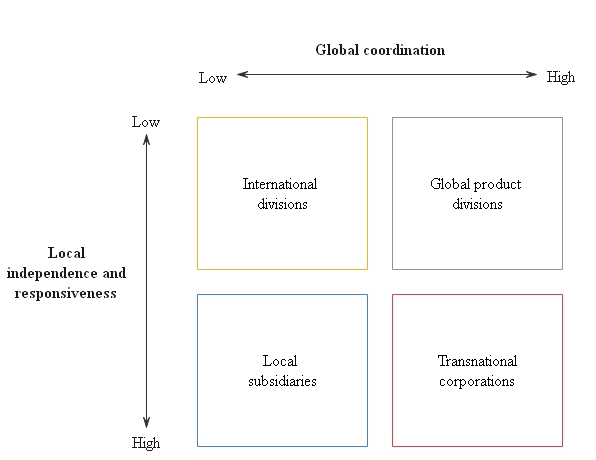
6. The team-based structure
A team-based organizational structure bunches employees as per team. A team organizational structure is intended to disturb the conventional chain of command, concentrating more on critical thinking, collaboration, and giving employees more control.
Pros
- Builds profitability, execution, and straightforwardness by separating storehouses
- Advances a development mentality
- Qualities experience instead of status
- Requires insignificant management
- Fits well with deft organizations with scrum or tiger teams
Cons
- Conflicts with numerous organizations' common tendency of an only various leveled structure
- Might make particular ways less understood for employees
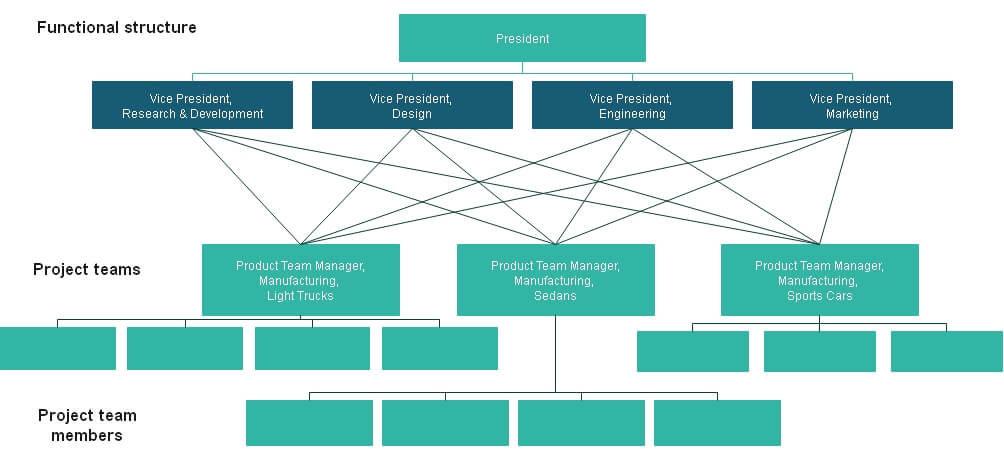
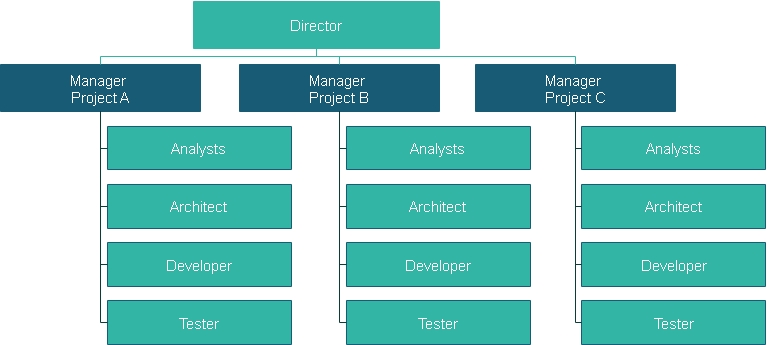
7. The project-based structure
A project-based structure is one where teams are created, undertake the work and are then dissolved. This can be particularly appropriate for organizations that deliver large, expensive and durable goods or services (civil engineering, information systems) or those delivering time-limited events – such as conferences, sporting events or even management development programs.
Pros
- Effectiveness: The structural flexibility facilitates the allocation of physical and human resources to endeavors that are of most benefit to the organization.
- Equality: The chances of internal politics and favoritism reduce to a great extent.
- Flexibility: The response time and flexibility improves because the manager has direct authority over project operations.
Cons
- When employees keep shifting from one project to another, career continuity might be a problem.
- With less communication between teams, knowledge transfer is also a challenge.
Wrapping up with Tips & Tricks
The ones that appeared above are the most usually utilized organization outline structure types or organogram structure types, as some call them. Yet, there are more models with different focal points based on circumstance and association. You can make without much of a stretch analysis with various models utilizing organization diagram programming, just like we did with EdrawMax.
It is a userfriendly application that you can easily download and use with free features. Make organizational structures for your company and win your way to the front.