What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Part 1: What is a Value Chain?
- Part 2: History of Value Chain
- Part 3: Advantages of Value Chain
- Part 4: Value Chain used in what fields or areas
- Part 5: Main Value Chain Analysis Activities
- Part 6: How to Use the Value Chain Analysis Model?
- Part 7: Further Value Chain Analysis Tips
- Part 8: Example
- Part 9: More Free Value Chain Analysis Templates
Part 1: What is a Value Chain?
What is Value Chain Analysis? A value-chain analysis aims to increase production efficiency to deliver maximum value with the least possible cost.
A value chain describes the full range of activities needed to add value for the company by transforming the inputs into a product or service. For the manufacturing industry, the value chain involves the steps starting from conception to product distribution. While in the services industry, it may include measures to provide a service.
Value-chain analysis in a company is conducted by evaluating the entire process involved along with each step. The final required result of Value Chain Analysis is a more competitive, efficient business with a competitive edge over others.
Part 2: History of Value Chain
What is value chain analysis's history?
The value chain has evolved to come to its current structure. The ‘filière concept’ was introduced in the 1960s at the Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique (INRA) and the Centre Internationale en Recherche Agronomique pour le Développement (CIRAD). It was an analytical tool for empirical agricultural research. It helped create a more structured understanding of the economic processes of farming commodities within production and distribution systems.
On the other hand, the general filière concept applies to the domestic value chains.
In 1974, Wallerstein developed the concept of commodity chains. They designed this concept around the world systems theory, which is an elaboration of the dependency theory. This concept of a commodity chain further developed into a global commodity chain by Gereffi and others.
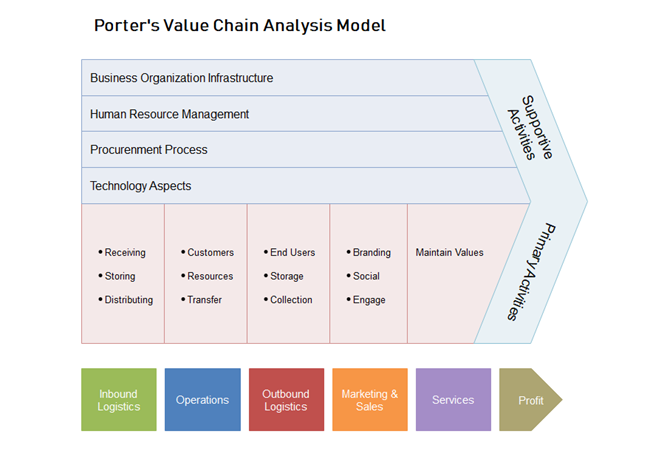
Micheal Porter introduced the concept of the value chain in the 1980s. He discussed Value Chain Analysis in terms of competitive advantage. Porter's value chain has two primary types of activities that support each other to add value to the company's input to transform it into cost-effective outputs. These two types of activities are ;
- Primary activities
- inbound logistics
- Operations
- Outbound logistics
- Marketing
- Sales
- Support activities
- Strategic planning
- Human resource management
- Technology development
- Procurement
Part 3: Advantages of Value Chain
Are you wondering what are Value Chain Analysis's advantages ? Let us discuss this in detail.
- Value Chain Analysis can play an instrumental role in introducing a structure to any business regardless of the industry and the size. When everything follows a system, there is a predictability and continuous improvement process that leads the company to a competitive advantage over peers.
- Value Chain Analysis promotes cross-functional teams for planning, research, development, and delivery. This means that simultaneous projects for different products or even for the same product can be conducted. This approach produces efficiency, cost reduction, and quality improvement.
- If you ask, what is Value Chain Analysis's primary purpose? One unanimous answer will be to introduce repeatable and measurable business processes for value addition. Value Chain Analysis covers the whole lifespan from conception to implementation and delivery to reduce overall operational inefficiencies and waste resources.
- Value Chain Analysis also handles the inputs and raw materials through its procurement part. It manages vendors to avoid delays, performance, or quality lapses.
- Reduced inefficiencies, standardized processes, and decreased time-lapses guarantee reduced costs. The management can later investigate these performance and cost savings for maximized profitability.
- The ultimate result of a comprehensive and efficient Value Chain Analysis is improved profitability and tremendous overall success.
Part 4: Value Chain used in what fields or areas
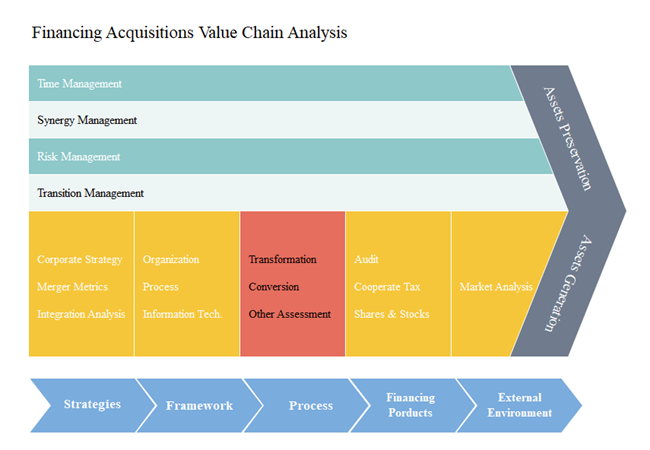
Value Chain Analysis can be used in nearly all fields and industries including manufacturing (automobiles etc.), trade, retail (supermarkets etc.), logistic, finance (online banking etc.). So far, many world top 500 companies, such as FedEx, Toyota, Walmart and Nestle etc., integrate the basic Value Chain Analysis models for the changing market demand. Here is an example of Value Chain Analysis in the finance sector (click on the image to see more).
Some particular use cases are:
- Food Business
- Information Technology
Food businesses, including frozen foods and cooked tinned food, may use Value Chain Analysis to ensure that they meet food safety standards and provide the best services. This is important because it has strict government standards to be completed, including hygiene and temperature maintenance.
Software developers use Value Chain Analysis to identify the bugs and issues in their software products like online order tracking, system program testing, and inventory management systems. Value Chain Analysis is pivotal in ensuring bug-free softwares and timely delivery.
Part 5: Main Value Chain Analysis Activities
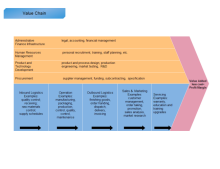
In reality, firms may undertake thousands of activities in producing goods or services. According to Porter, all of these activities can be put into two general common groups: the primary activities and the support activities. Companies can gain more profit if combing these two activities efficiently. Porter's theory can be drawn as a diagram below:
Primary Activities
These activities have direct relationship with creating and delivering a product, and they are usually considered as the main source of cost advantage where costs can be quickly found. Primary activities have five sub-categories:
- Inbound logistics refers to the receive, storage and distribution of raw resources during the production process. Here supplier relationships plays an important role.
- Operations is the process (assembling, packaging etc.) at which the raw resources are turned into the final service or product. At this stage value is added to the product through the production line.
- Outbound logistics is the distribution of the final product to consumers, wholesalers or retailers etc. At this stage your operational systems create value.
- Marketing and sales including activities such as advertising, promoting, selling, analyzing market and pricing the final product to ensure it is targeted to the appropriate consumer groups. The key aim is to make your customer groups aware of the product in order to create demand for it. At this stage, you should focus on consumer relationship management.
- Service refers to the activities (warranty and ater-sale services etc.) needed to improve or maintain your service's or product's performance after ordering.
Support Activities
Organizations usually use support activities with the primary activities to gain profit. Support activities also used as the most key source of differentiation advantage. Furthermore, each support activity can be used in each primary activity. There are four main sub-groups of support activities as shown below:
- Infrastructure refers to organizational management, risk management, accounting, legal, and quality-control mechanisms for productive daily operations. Inefficient infrastructures would lead to the waste of organizational resources and a lower level of productivity.
- Human resource management mainly refer to hire, train, compensate, and retain proper professional employees. In service sectors where face-to-face interactions commonly exist, employees can be the competitive advantages of their firms.
- Procurement is how the raw resources (machinery items etc.) for the product or service are obtained. Procurement normally involves finding vendors, managing suppliers' relationships, and negotiations based on agreements. The biggest challenge for purchasing is to get suitable quality at the best price according to the budget.
- Technology is used by firms in many ways to research, design, improve and develop new production and reduce cost. In modern times, technical development may require high level of expenditure and long time, but organizations can therefore enjoy long-term benefits and gain more values.
Part 6: How to Use the Value Chain Analysis Model?
Cost advantage and differentiation advantage are two key approaches for undertaking a Value Chain Analysis for a whole producing line or process.
Cost Advantage
This method is used when firms want to analyze the sources of their cost advantages, and the factors that drive these costs. A typical cost advantage approach has the following five steps:
1. Find out the organization's primary and support activities by deeply looking into capabilities of the organization (e.g. direct-selling activities and indirect-selling activities).
2. Break down the total costs of producing a product or service and assign to each activity.
3. Explore cost drivers for each activity (economics of scale, organizational policies, location, and labor-intensive activities etc.).
4. Analyze the relationships between different activities (e.g. the reason of cost reduction).
5. Find out any breakpoints to reduce costs (e.g. outsourcing).
Differentiation Advantage
This method is used when organizations want to create superior products or services compared to their competitors in the market. A general differentiation advantage has the following three steps:
1. Find out the customers' value-generating activities, for example, the outstanding product functions by a leading company.
2. Integrate strategies (e.g. competitor analysis, human resource management, technology innovation, customer relationship management) to improve user experience, customer service and more.
3. Look for the best sustainable choice of product/service differentiation and achieve them in a step-by-step way.
Part 7: Further Value Chain Analysis Tips
What are Value Chain Analysis' challenges? Well, there are many. You and your team have to ponder how to identify relevant process areas, connections between primary and secondary activities, cost vs. benefit analysis, and identify competitive advantage. Here are some tips to help you.
- First, decide whether you are looking for a competitive advantage or differential.
- Involve your time in the process. Every department must have a representation in your value chain group.
- Look out for customer reaction and satisfaction.
- Keep a monitoring mechanism in place.
- Be ready for change.
Part 8: Example
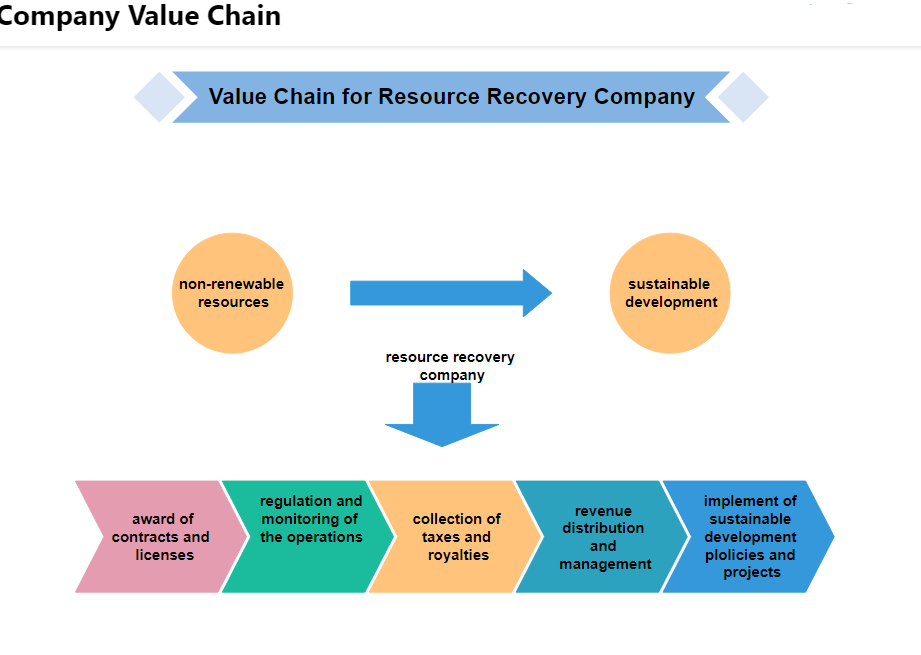
This value chain of a recovery company shows the competitive advantage gained through the transition from a non-renewable resource to sustainable development. The resource recovery company starts the process by awarding the contracts and licenses. The later steps are regulation and monitoring of the operations. The implementation of sustainable development policies and projects is conducted after getting correct data or statistics for the revenue distribution from the management department.
Part 9: More Free Value Chain Analysis Templates
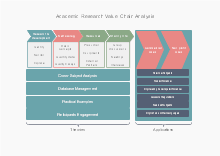
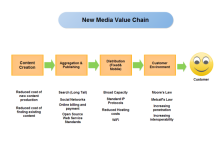
Free download templates are available below to help your team determine and analyze value chains in different sectors. Click on any of these to see more details.
|
|
|
| Academic Research VCA Template | New Media VCA Template | Profit VCA Template |